coolliyong.github.io
链表
维基百科定义:
链表(Linked list)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是并不会按线性的顺序存储数据,而是在每一个节点里存到下一个节点的指针(Pointer)。由于不必须按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到 O(1)的复杂度,比另一种线性表顺序表快得多,但是查找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要 O(n)的时间,而顺序表相应的时间复杂度分别是 O(logn)和 O(1)。
使用链表结构可以克服数组链表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。但是链表失去了数组随机读取的优点,同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大。
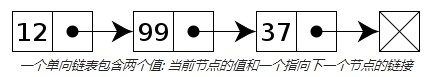
单向链表
链表中最简单的一种是单向链表,它包含两个域,一个信息域和一个指针域。这个链接指向列表中的下一个节点,而最后一个节点则指向一个空值。
class LinkList {
constructor() {
this.head = null
this.length = 0
}
/**
* 静态方法,创建节点
* @param data
* @returns
*/
static createNode(data) {
return {
data,
next: null
}
}
/**
* 添加节点到链表尾部
* @param data
*/
append(data) {
const node = LinkList.createNode(data)
if (this.length === 0) {
this.head = node
} else {
let cur = this.head
while (cur.next) {
cur = cur.next
}
cur.next = node
}
this.length += 1
}
/**
* 根据位置信息删除节点 返回数据
* @param position
*/
removeat(position) {
if (position >= this.length || position < 0) return null
let data
if (position === 0) {
data = this.head
this.head = this.head.next
this.length--
return data
}
// 当前指针
let cur = this.head.next
// 上一个指针
let prev = this.head
let idx = 1
while (cur) {
if (idx === position) {
data = cur
prev.next = cur.next
this.length--
return data
}
// cur,prev 各往后移一位
prev = cur
cur = cur.next
idx++
}
return null
}
/**
* 根据数据删除元素 返回索引
* @param data
* @returns
*/
remove(data) {
// 当前指针
let cur = this.head
// 上一个指针 默认从head 开始 这样如果 删除的是第一个元素 那么 prev 也不是一个野指针
let prev = this.head
let idx = 0
while (cur) {
if (data === cur.data) {
prev.next = cur.next
this.length--
return idx
}
// cur,prev 各往后移一位
prev = cur
cur = cur.next
idx++
}
return null
}
/**
* 根据位置信息插入数据 返回长度
* @param position
* @param data
* @returns {number}
*/
insert(position, data) {
if (position > this.length || position < 0) return -1
const node = LinkList.createNode(data)
// 头插和尾插为单独场景
if (position === 0) {
node.next = this.head
this.head = node
this.length += 1
return this.length
} else if (position === this.length) {
let cur = this.head.next
while (cur.next) {
cur = cur.next
}
cur.next = node
this.length += 1
return this.length
}
let cur = this.head
let prev = this.head
let idx = 1
while (cur) {
if (idx === position) {
node.next = cur.next
prev.next = node
this.length += 1
return this.length
}
prev = cur
cur = cur.next
idx++
}
}
/**
* 根据数据返回索引
* @param data
*/
find(data) {
let idx = 0
let cur = this.head
while (cur.next) {
if (cur.data === data) {
return idx
}
idx++
cur = cur.next
}
return -1
}
toString() {
let resultString = ''
const cur = this.head
while (cur) {
resultString += cur.data + ' ,'
}
return resultString
}
}
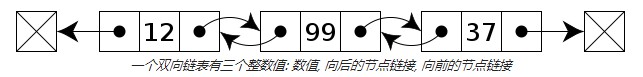
双向链表
一种更复杂的链表是“双向链表”或“双面链表”。每个节点有两个连接:一个指向前一个节点,(当此“连接”为第一个“连接”时,指向空值或者空列表);而另一个指向下一个节点,(当此“连接”为最后一个“连接”时,指向空值或者空列表)
class DoubleLinkList {
constructor() {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
this.length = 0
}
/**
* 静态方法,创建节点
* @param data
* @returns
*/
static createNode(data) {
return {
data,
next: null,
prev: null
}
}
/**
* 插入到尾部
* @param data
*/
append(data) {
const node = DoubleLinkList.createNode(data)
if (this.length === 0) {
this.head = node
this.tail = node
} else {
// const cur = this.head
// 节点的上一个是 老的尾链
node.prev = this.tail
// 老的尾链的下一个是新节点
this.tail.next = node
// 更新尾链接
this.tail = node
}
this.length += 1
}
forwardingString() {
let cur = this.head
let resultStr = ''
while (cur) {
resultStr += cur.data
cur = cur.next
}
return resultStr
}
backingString() {
let cur = this.tail
let resultStr = ''
while (cur) {
resultStr += cur.data
cur = cur.prev
}
return resultStr
}
/**
*
* @param position
* @param data
*/
insert(position, data) {
if (position > this.length || position < 0) throw new Error('position越界')
const node = DoubleLinkList.createNode(data)
if (position === 0) {
this.head.prev = node
node.next = this.head
this.head = node
this.length += 1
return this.length
} else if (position === this.length) {
this.tail.next = node
node.prev = this.tail
this.tail = node
this.length += 1
return this.length
} else {
const len = this.length
// 使用一下二分判断,再决定从头或尾部遍历
const flag = len - position > len / 2 ? 'prev' : 'next'
let idx = flag === 'next' ? 0 : this.length - 1
let cur = flag === 'next' ? this.head : this.tail
while (cur[flag]) {
if (idx === position) {
// 需要处理三个节点
// 当前节点的上一个 next 指向 node
cur.prev.next = node
// 节点 替代 当前的 prev
node.prev = cur.prev
// 节点插入到当前节点前
node.next = cur
// 当前节点 的prev 指向 node
cur.prev = node
this.length += 1
return this.length
}
cur = cur[flag]
if (flag === 'next') {
idx++
} else {
idx--
}
}
}
}
/**
* 根据数据删除元素 且返回索引
* 无法判断元素在哪,只能以此遍历
* @param data
*/
remove(data) {
let cur = this.head
let idx = 0
while (cur.next) {
if (cur.data === data) {
if (idx === 0 && this.length === 0) {
// 移除第一个 但是链表只有一个
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else if (idx === this.length) {
// 移除末尾元素
this.tail = cur.prev
this.tail.next = null
} else if (idx === 0) {
// 移除链头元素
this.head = cur.next
} else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next
cur.next.prev = cur.prev
}
this.length -= 1
return idx
}
cur = cur.next
idx += 1
}
return false
}
}
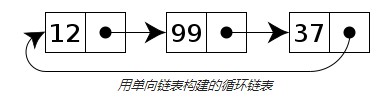
循环链表
在一个 循环链表中, 首节点和末节点被连接在一起。这种方式在单向和双向链表中皆可实现。要转换一个循环链表,你开始于任意一个节点然后沿着列表的任一方向直到返回开始的节点。再来看另一种方法,循环链表可以被视为“无头无尾”。这种列表很利于节约数据存储缓存, 假定你在一个列表中有一个对象并且希望所有其他对象迭代在一个非特殊的排列下。
指向整个列表的指针可以被称作访问指针。
2. 两数相加
-
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
-
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
-
您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
示例:
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var addTwoNumbers = function(l1, l2) {
let current = l1
let current2 = l2
// 进一位数字
let carried = 0
// 新建一个空链表
const head = new ListNode(-1)
let curH = head
let result = 0
while (current || current2) {
result =
(current ? current.val : 0) + (current2 ? current2.val : 0) + carried
carried = parseInt(result / 10)
curH.next = new ListNode(result % 10)
curH = curH.next
current = current ? current.next : null
current2 = current2 ? current2.next : null
}
// 最后 如果 进位标识 还有值,则 需要在添加一个节点到尾部
// 链表尾 的节点不可能大于100
if (carried > 0) {
curH.next = new ListNode(carried)
}
return head.next
}
19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
解题思路
- 没有length 属性,无法得知链表长度, 所以也无从得到倒数第二个是谁,所以首先线性遍历一次,先得到链表总长度O(N)
- 然后再做删除操作,又线性查找一次
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let len = 0
// 临时指针
let cur = head
while (cur) {
len++
if (cur.next) cur = cur.next
else cur = null
}
if(n === len){
head = head.next
return head
}else{
cur = head
let prev = head
let idx = 0
while(head.next){
if(n === len - idx){
prev.next = cur.next
return head
}
idx += 1
prev = cur
cur = cur.next
}
}
};