coolliyong.github.io
字典(关联数组)
维基百科解释:
在计算机科学中,关联数组(英语:Associative Array),又称映射(Map)、字典(Dictionary)是一个抽象的数据结构,它包含着类似于(键,值)的有序对。一个关联数组中的有序对可以重复(如C++中的multimap)也可以不重复(如C++中的map)。备关联数组特性的数据结构。解决字典问题的常用方法,是利用散列表,但有些情况下,也可以直接使用二叉查找树或其他结构
字典问题是设计一种能够具备关联数组特性的数据结构。解决字典问题的常用方法,是利用散列表,但有些情况下,也可以直接使用二叉查找树或其他结构。
百度百科解释:
JavaScript的对象本质就是一个关联数组。
关联数组和数组类似,由以名称作为键的字段和方法组成。
javascript数据结构和算法描述:
集合、字典和散列表可以存储不重复的值。在集合中,我们感兴趣的是每个值本身,并把它当作主要元素。在字典中,我们用[键,值]的形式来存储数据。在散列表中也是一样(也是以[键,值]对的形式来存储数据)。但是两种数据结构的实现方式略有不同,本章中将会介绍。
集合表示一组互不相同的元素(不重复的元素)。在字典中,存储的是[键,值]对,其中键名是用来查询特定元素的。字和集合很相似,集合以[值,值]的形式存储元素,字典则是以[键,值]的形式来存储元素。字典也称作映射。
function Dictionary() {
this.item = {}
}
Dictionary.prototype.set = function(key, val) {
this.item[key] = val
}
Dictionary.prototype.has = function(key) {
return this.item.hasOwnProperty(key)
}
Dictionary.prototype.get = function(key) {
if (this.has(key)) {
return this.item[key]
}
}
Dictionary.prototype.delete = function(key) {
if (this.has(key)) {
delete this.item[key]
return true
}
return false
}
Dictionary.prototype.keys = function(key) {
return Object.keys(this.item)
}
Dictionary.prototype.values = function(key) {
return Object.values(this.item)
}
Dictionary.prototype.size = function() {
return Object.keys().length
}
const coolliyong = new Dictionary()
coolliyong.set('github', 'coolliyong.github.io')
coolliyong.set('email', 'liyong857637472@163.com')
coolliyong.set('language', 'javascript')
console.log(coolliyong.has('address')) // false
console.log(coolliyong.get('email')) // liyong857637472@163.com
console.log(coolliyong.keys()) // [ 'github', 'email', 'language' ]
console.log(coolliyong.values()) // [ 'coolliyong.github.io', 'liyong857637472@163.com', 'javascript' ]
散列
维基百科定义:
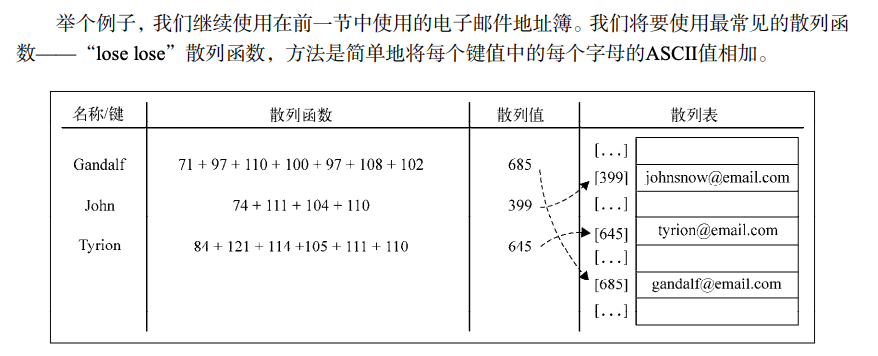
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表 HashMap ),是根据键(Key)而直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。也就是说,它通过计算一个关于键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,这加快了查找速度。这个映射函数称做散列函数,存放记录的数组称做散列表。
一个通俗的例子是,为了查找电话簿中某人的号码,可以创建一个按照人名首字母顺序排列的表(即建立人名 x 到首字母 F(x)的一个函数关系), 在首字母为
W的表中查找“王”姓的电话号码,显然比直接查找就要快得多。这里使用人名作为关键字,“取首字母”是这个例子中散列函数的函数法则 F(), 存放首字母的表对应散列表。关键字和函数法则理论上可以任意确定。
散列函数(哈希函数)
散列函数(英语:Hash function)又称散列算法、哈希函数,是一种从任何一种数据中创建小的数字“指纹”的方法。散列函数把消息或数据压缩成摘要,使得数据量变小,将数据的格式固定下来。该函数将数据打乱混合,重新创建一个叫做散列值(hash values,hash codes,hash sums,或 hashes)的指纹。散列值通常用一个短的随机字母和数字组成的字符串来代表。好的散列函数在输入域中很少出现散列冲突。在散列表和数据处理中,不抑制冲突来区别数据,会使得数据库记录更难找到。
需要实现的方法
- 常见实现:
数组 + 链表 - 常见实现:
数组 + 二叉树
代码实现
- put(key,value):向散列表增加一个新的项(也能更新散列表)。
- remove(key):根据键值从散列表中移除值。
- get(key):返回根据键值检索到的特定的值。
function HashMap() {
this.table = []
}
HashMap.prototype.put = function(key, val) {
const _key = this.loseloseHashCode(key)
this.table[_key] = val
}
/**
* 简单的散列函数
* @param {String} key
* @returns {String}
*/
HashMap.prototype.loseloseHashCode = function(key) {
let hash = 0
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i)
}
return hash % 37
}
HashMap.prototype.get = function(key) {
const _key = this.loseloseHashCode(key)
if (this.has(_key)) {
return this.table[_key]
}
}
HashMap.prototype.remove = function(key) {
const _key = this.loseloseHashCode(key)
if (this.has(_key)) {
this.table[_key] = undefined
return true
}
}
HashMap.prototype.has = function(key) {
return this.table[key] !== undefined
}
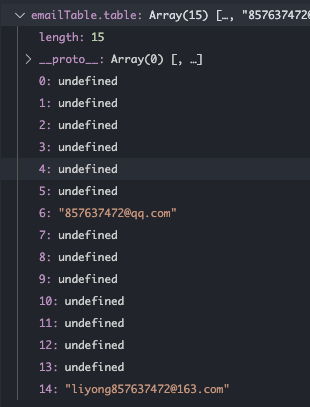
const emailTable = new HashMap()
emailTable.put('coolliyong', 'liyong857637472@163.com')
emailTable.put('qqemail', '857637472@qq.com')
console.log(emailTable.get('coolliyong')) // liyong857637472@163.com
console.log(emailTable.get('qqemail')) // 857637472@qq.com
console.log(emailTable.get('999')) // undefined
冲突处理
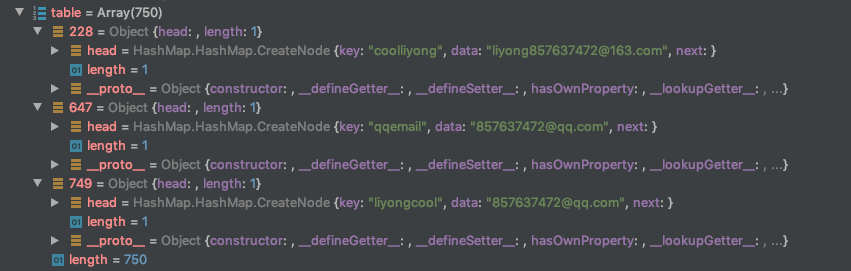
以上是基于数组 + 散列函数 来实现,这时候可能会产生冲突,如果我弟弟的名字是 liyongcool (名字一样,顺序不同),散列函数算出来的结果是一致的,然后他就覆盖了我的邮箱…这就是冲突
emailTable.put('liyongcool', '857637472@qq.com')
console.log(emailTable.get('coolliyong')) // 857637472@qq.com
- 解决办法
- 单独链表法(拉链法): 数组 + 链表 ```javascript // coolliyong 在数组的位置是 14 liyongcool也是14 // 数组 14 的位置是一个链表 14 head -> 所以用链表链起来
const hashMap = [ undefined, // 0 undefined, // 1 undefined, // 2 undefined, // 3 undefined, // 4 undefined, // 5 undefined, // 6 undefined, // 7 undefined, // 8 undefined, // 9 undefined, // 10 undefined, // 11 undefined, // 12 undefined, // 13 { key: ‘coolliyong’, value: ‘liyong857637472@163.com’, next: { key: ‘liyongcool’, value: ‘857637472@qq.com’, } } ] // 缺点:如果14这个 索引 的值过多,那么一级一级往下查找,也会很慢
2. 开放空间法 还是使用数组,还是刚刚这个问题,如果 第二个key 也是14,插入的时候发现14这个坑已经被占用了,那么坑往后找,找到空位就往里填
```javascript
const hashMap = [
undefined, // 0
undefined, // 1
undefined, // 2
undefined, // 3
undefined, // 4
undefined, // 5
undefined, // 6
undefined, // 7
undefined, // 8
undefined, // 9
undefined, // 10
undefined, // 11
undefined, // 12
undefined, // 13
'liyong857637472@163.com', // 14
'857637472@qq.com',// 15
]
个人觉得这种方式很憨批,假如我有一有哈希表,里面只有 3 个冲突,14 冲突,其他所有的都不冲突,这时候,我所有的规律都乱了,差不多所有的查找 = hashCodeFn(key) + 3
但是这种方式优于拉链法的地方就是内存合理化更高,不需要数组一直扩容。
创建更好的散列函数
这种简单粗暴的散列方法会可能会造成大量的冲突,好的散列函数不应该转化出许多相同的结构
一个表现良好的散列函数是由几个方面构成的:插入和检索元素的时间(即性能),当然也包括较低的冲突可能性。
改用djb2HashCode来处理
function djb2HashCode(key) {
var hash = 5381; //{1}
for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) { //{2}
hash = hash * 33 + key.charCodeAt(i); //{3}
}
return hash % 1013; //{4}
};
它包括初始化一个hash变量并赋值为一个质数(行{1}——大多数实现都使用5381),然后 迭代参数key(行{2}),将hash与33相乘(用来当作一个魔力数),并和当前迭代到的字符的ASCII 码值相加(行{3})。
最后,我们将使用相加的和与另一个随机质数(比我们认为的散列表的大小要大——在本例 中,我们认为散列表的大小为1000)相除的余数。
在尝试一下上面的例子,得到以下结果
这并不是最好的散列函数,但这是最受社区推崇的散列函数之一。
-《 JavaScript 数据结构和算法》
ES6——Map 类
const map = new Map();
map.set('coolliyong', 'liyong857637472@163.com')
map.set('liyongcool', '857637472@qq.com')
console.log(map)
//Map {
// 'coolliyong' => 'liyong857637472@163.com',
// 'liyongcool' => '857637472@qq.com'
//}
增删改
-
Map.prototype.set(key,value): 设置元素修改元素 -
Map.prototype.delete(key): 删除元素 -
Map.prototype.has(key): 是否存在 Map.prototype.size:获取长度Map.prototype.clear(): 清空
遍历方法
Map.prototype.keys():返回键名的遍历器。Map.prototype.values():返回键值的遍历器。Map.prototype.entries():返回所有成员的遍历器。Map.prototype.forEach():遍历 Map 的所有成员。